2025 moisture conditions in many Prairie regions were dry in late May and early to mid June. However, recent rainfall in some regions over the last 1-2 weeks increases the risk of development of leaf spot diseases in barley and wheat. Although crop rotation and variety resistance are useful strategies, rotations typically need to be at least two years between host crops. In addition, the variety being grown may not have a disease resistance package that covers all leaf diseases. As a consequence fungicide application becomes a key tool for managing cereal leaf disease risk.
Scouting is key to identifying emerging cereal leaf disease issues and the need for one or more in-crop fungicide applications. Initially when scouting for weeds, producers and consultants can note the presence and level of leaf disease. This gives you a heads up in terms of a developing issue and the potential need to spray a fungicide as the crop progresses from stem elongation to flag and head emergence. Although there may be interest in applying fungicide at a herbicide timing, research indicates it will likely be of limited value in terms of protection of upper canopy leaves.
- https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/full/10.1139/cjps-2020-0318
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/07060660409507174
https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/10.4141/cjps-2014-364
- Exceptions occur with cereal rust diseases, especially stripe rust, where a herbicide timing application can be more useful. This is likely due to the biotrophic nature (i.e. they derive nutrients from living host tissues) of the rust pathogens and that initial rust inoculum typically comes from outside the crop, especially for spring cereals
- In contrast, cereal leaf spot diseases (scald, net blotch, spot blotch, tan spot, septorias) are necrotrophic in nature (i.e. the derive nutrients from dead plant tissue), while initial inoculum typically comes from old crop residues in the same field where the crop is growing
- Fungicide movement to the rust pathogen in living host tissues may be more extensive versus through dead plant tissues in the case of necrotrophic leaf spot pathogens. In addition, cereal leaf spot inoculum is continuously produced from old crop residues and thus can infect any new leaves that emerge after spraying has occurred
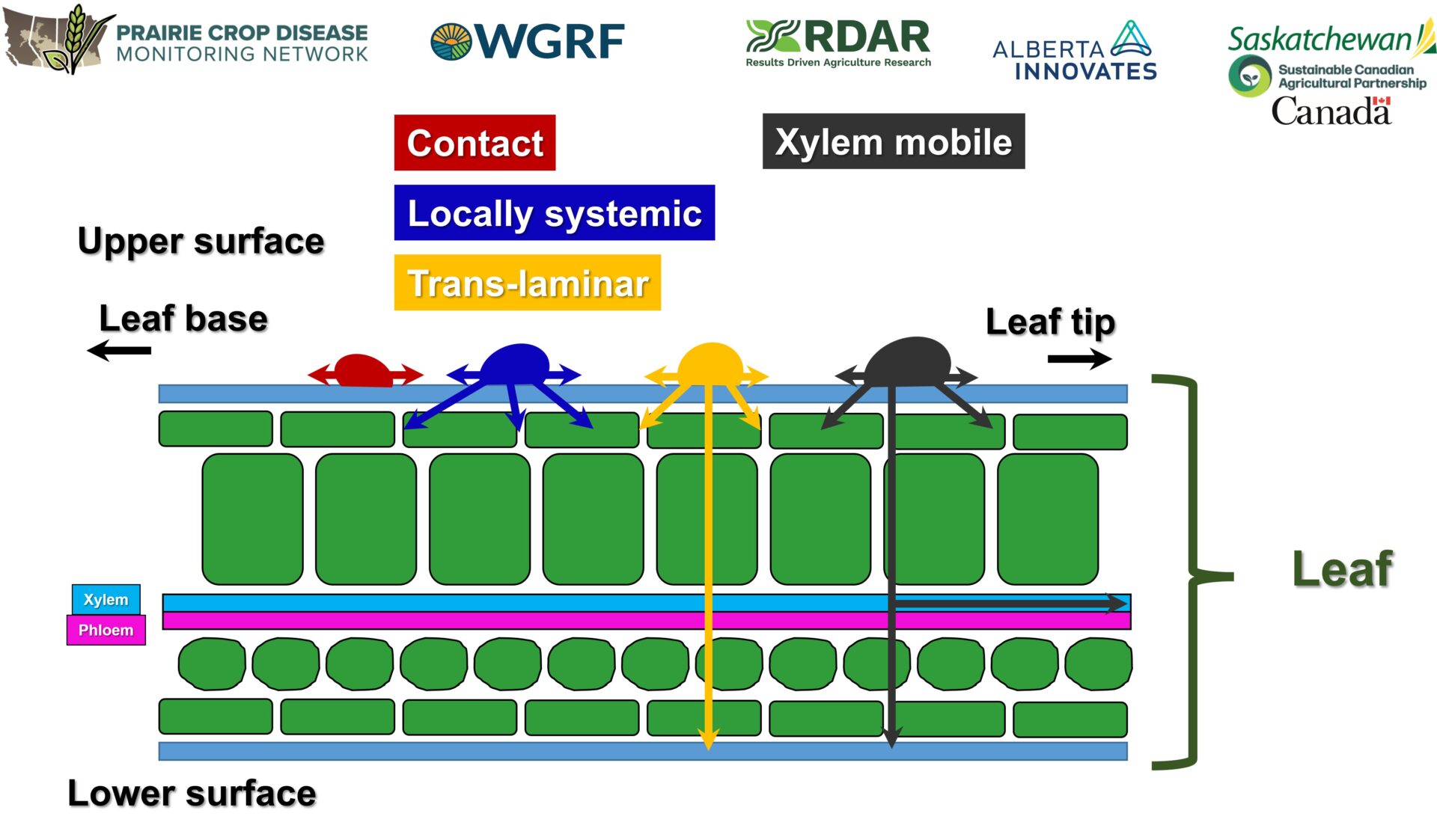
- Given the nature of fungicides, movement within plant is typically limited, but with more mobile actives they are typically xylem mobile and thus need to be applied directly to the plant tissues that need protection, i.e. upper canopy leaves aka “The Money Leaves” (term coined by Nick Poole, Field Applied Research (FAR) Australia)
- Fungicides do not generally have good eradicant activity, especially on mature established infections that are already 1-2 weeks old
- Thus, fungicides may not kill the leaf spot pathogens in well-established infections, although they may suppress/delay pathogen development and sporulation, but only for about 2-3 weeks
- After this period the leaf spot pathogens can resume growth and sporulation and thus contribute to subsequent disease development
Should producers decide to use fungicides at a herbicide timing, if leaf spot risk remains moderate to high from stem elongation to head emergence, they may need to spray again from flag leaf emergence to just after head emergence to protect key upper canopy tissues
- One or more factors related to an increased risk of early leaf spot development and the potential need for both pre- and post-head emergence fungicide applications
- Highly favourable weather conditions have occurred in the latter part of May and throughout June, e.g. moderate temperatures and frequent rain
- A susceptible crop variety (S-MS rating) is being grown
- A wheat on wheat or barley on barley rotation is being used
- Note a single year of a non-host crop between wheat or barley crops may not be enough when
- The variety is highly susceptible
- You noted moderate to high levels of leaf spot development in your previous wheat or barley crop
- Highly favourable weather conditions have occurred
- Note a single year of a non-host crop between wheat or barley crops may not be enough when
- One or more factors related to a reduced risk of early leaf spot development and where the main focus is on a post-head emergence fungicide application
- May and early-mid June have been dry, but then more favourable weather conditions occur during the latter half of June and into July
- e.g. moderate temperatures and frequent rain
- A variety with a minimum disease resistance rating of intermediate (MRMS) is being grown
- A rotation with a least a single year of a non-host crop between wheat or barley crops is being used
- You noted limited to low levels of leaf spot development in your previous wheat or barley crop
- Your main concern is suppression of fusarium head blight in terms of fusarium damaged kernels and deoxynivalenol (DON) contamination of grain
- May and early-mid June have been dry, but then more favourable weather conditions occur during the latter half of June and into July
- One or more factors related to a reduced risk of leaf spot development during the growing season and where a fungicide application will likely not be economical
- Dry conditions occur throughout the growing season, but especially in June and July
- Hot and dry conditions during June and July have an overwhelming impact on leaf spot risk regardless of variety resistance and rotation
- A variety with a minimum disease resistance rating of moderately resistant or resistant (MR or R) is being grown
- You are following a rotation with a least a two or more years of a non-host crop between wheat or barley crops
- You noted limited levels of leaf spot development in your previous wheat or barley crop
- The Prairie fusarium head blight (FHB) risk maps indicate low risk from flag leaf emergence to the grain filling period
- Dry conditions occur throughout the growing season, but especially in June and July
Keep in mind that as the number of in-season fungicide applications increases so does the risk of fungicide resistance development!
- If producers need to spray fungicide in a crop more than once during the growing season they need to implement strategies to limit the risk of fungicide resistance development
- Only spray if needed, limit the number of applications, rotate actives, and use products with multiple modes of action
- Here are some great resources in relation to managing the risk of fungicide resistance
- https://manageresistancenow.ca/disease/dfs-how-to-manage-fungicide-resistance-in-your-crops/
- https://cropprotectionnetwork.org/web-books/fungicide-use-in-field-crops?section=44-fungicide-resistance
- https://www.gov.mb.ca/agriculture/crops/guides-and-publications/pubs/guide-crop-protection-2025.pdf (see page 531)
- https://publications.saskatchewan.ca/api/v1/products/77706/formats/87089/download (see page 531)
- https://bluebook.print3connect.com/
As the crop moves towards flag leaf emergence, producers and consultants can use the extent of leaf disease development in the lower to upper canopy to gauge risk and fungicide need.
- The absence or limited appearance of symptoms (e.g. <1% leaf area affected or so) in the lower to middle canopy would generally indicate a low risk and thus limited need for fungicide
- However, things can change as the crop moves towards head emergence, so it is important to scout again
- Following head emergence if moderate disease levels are observed in the lower to middle canopy (e.g. >5-10% leaf area diseased) there is likely an emerging risk and need to spray a fungicide to protect key upper canopy leaves where most of your yield comes from
- This is especially true if wet conditions are expected from head emergence to the grain filling period
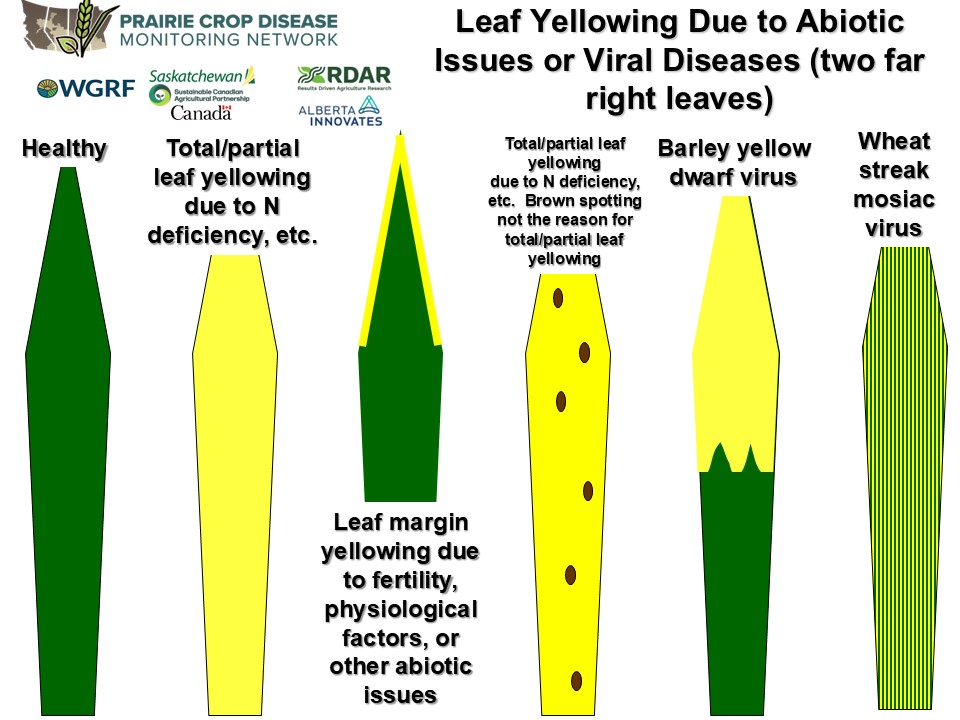
When scouting for cereal leaf diseases correct identification is critical.
- A variety of issues may produce leaf symptoms that may be incorrectly identified as fungal leaf diseases
- For example, general leaf yellowing is not indicative of the cereal leaf spots (e.g. tan spot and septoria in wheat, net blotch/scald/spot blotch in barley), but may reflect nutrient deficiencies, drought/heat stress or perhaps root disease issues
- Make sure the symptoms are actually caused by disease and not damage (burning, scalding, etc.) due to insect feeding, herbicides or foliar-applied fertilizers
- Physiological leaf spotting can be confused with cereal leaf spot symptoms and are typically related to chloride deficiency and sun damage
- For example, with sun damage in barley the most severe symptoms are on the upper canopy leaves, while chloride deficiency symptoms are found throughout the cereal canopy and may be associated with particular cereal varieties
- In contrast, cereal leaf spot symptoms generally follow a gradient, i.e. most severe in the lower canopy, but decrease as you move to the middle and upper canopies.
Here are some links to a previous PCDMN post on white flecking in wheat, and a recent Montana State University alert regarding differentiating physiological leaf spots from those caused by cereal leaf spot pathogens.
https://prairiecropdisease.blogspot.com/2022/06/unusual-symptoms-in-alberta-barley-and.html
https://www.montana.edu/cope/email-format/admin/view.php?draft=13640&uid=68261a2c4af5d7.78080120

Here are some links to PCDMN resources for cereal leaf spot identification:
Wheat:
- Speckled leaf blotch and mini info card
- Parastagonospora/Septoria leaf and glume blotch and mini card
- Tan spot and mini card
- Fusarium head blight and mini card
- Fusarium head blight seed infections
- Bacterial leaf streak and mini card
- Cereal rusts
Barley:
- Net-form net blotch in barley and mini card
- Spot-form net blotch in barley and mini card
- Scald in barley and mini card
- Spot blotch in barley and mini card
- Bacterial leaf streak and mini card
- Fusarium head blight and mini card
- Fusarium head blight seed infections
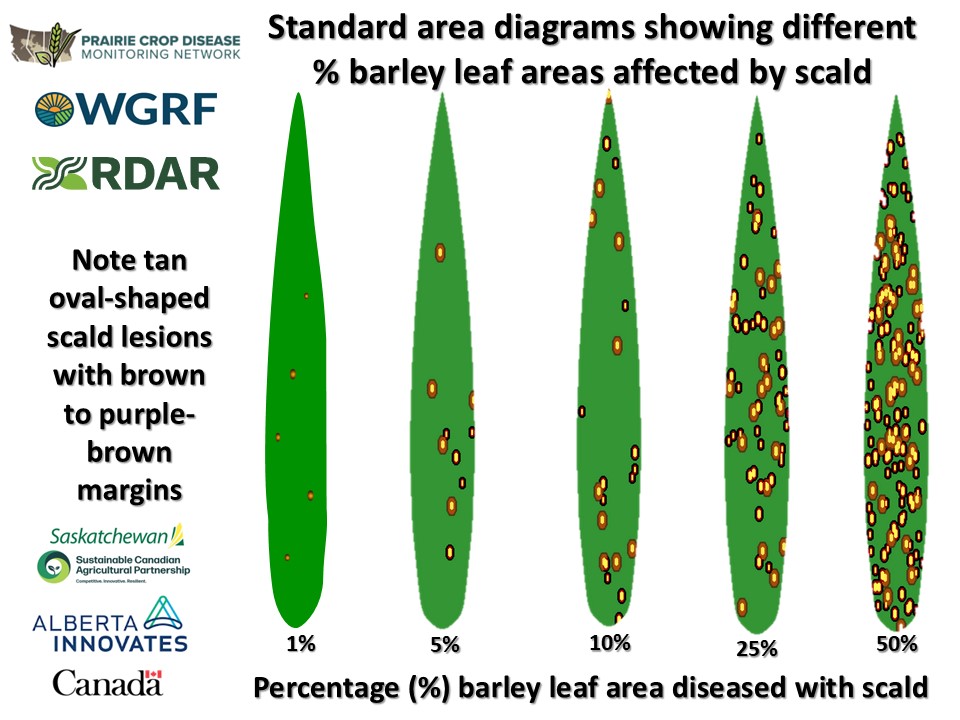
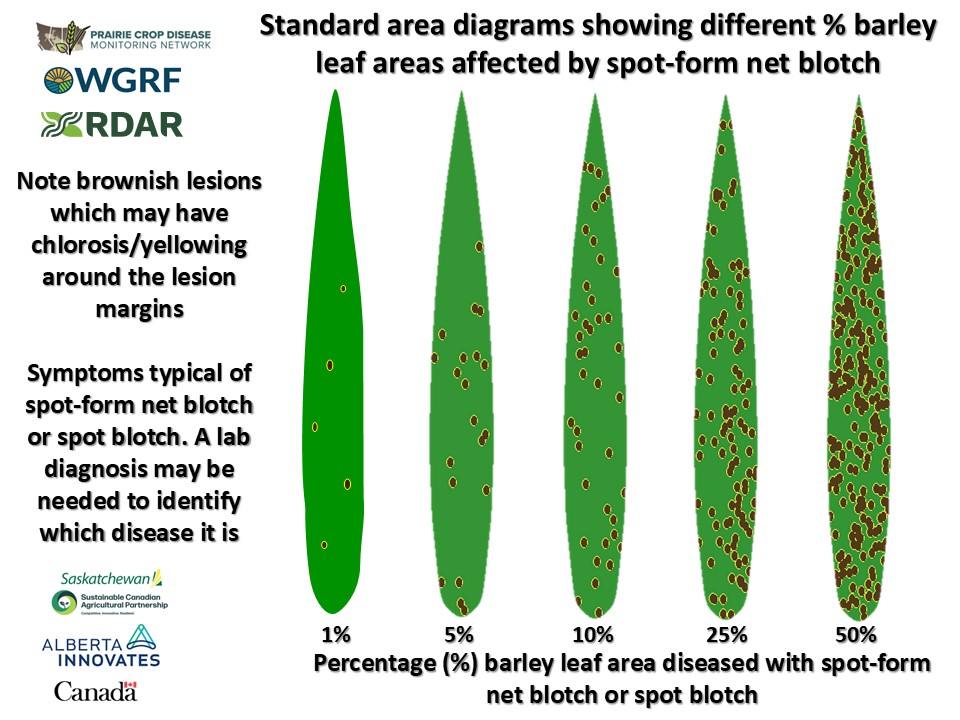
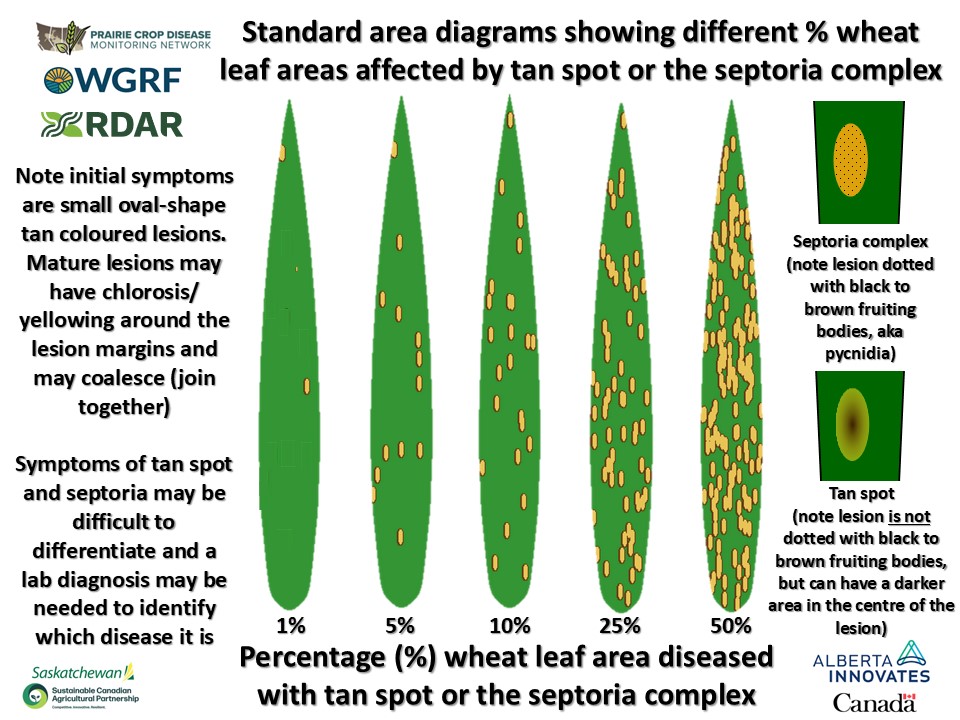
The use of standard area diagrams can help in terms of determining the level of leaf spot development.
- Here are some standard area diagrams showing 1, 5, 10, 25, and 50% of the leaf area affected with various leaf spot diseases in barley and wheat
- Note that symptoms of spot-form net blotch and spot blotch in barley can be difficult to distinguish without laboratory testing of plant samples
- In addition, differentiating tan spot from the septoria complex in wheat can be challenging even for experienced plant pathologists, and thus a lab diagnosis may be needed
- All cereal leaf spot diseases result in destruction of leaf tissues and thus affect grain yield and filling
- The goal should be correct identification of leaf spot disease issues and then assessment of their overall level, i.e. severity


It is important to put the level of disease into perspective.
- Trace to low levels of leaf disease from tillering to head emergence = limited risk, and thus a fungicide may not be needed, and if used can result in negative net returns
- In contrast, if you notice significant levels of disease during weed scouting, and increased severity in the lower to middle canopy at flag leaf emergence (especially on the third leaf from the head), a fungicide may be needed prior to head emergence, i.e. at or just before flag leaf emergence
- If leaf disease levels are absent or limited during weed scouting and at flag leaf emergence, you may be able to delay and only use one in-crop fungicide application after head emergence to provide leaf disease control and fusarium head blight suppression
- Lastly, a producer may have significant leaf disease development at stem elongation to flag leaf emergence and are also concerned about fusarium head blight and post head emergence leaf spot development
- In this situation more than one fungicide application may be needed, i.e. around flag leaf emergence plus again after head emergence
- Keep in mind that when you need to use more than one fungicide application during the growing season, make sure to use strategies to limit the risk of fungicide resistance development
Finally, keep in mind what the weather conditions are like as well as the disease resistance package in the cereal variety you are growing.
- Moderate temperatures, frequent rainfall and heavy dews increase the risk, especially with varieties that are not resistant to disease
- In contrast, with warm dry conditions and where the soil and crop canopy are dry in the morning, the risk of leaf spot development is limited and a fungicide is likely not needed (see wet pants test below)
- Fungicide response is generally greatest for cereal varieties that are susceptible to moderately susceptible
- In contrast, varieties that are moderately resistant to resistance are less responsive and may not need a fungicide application
- One caveat is that a typical crop may be faced with multiple leaf disease issues. Although a variety may be resistant to one disease, it may be susceptible to other diseases, and thus a fungicide may be needed depending on weather conditions and in-season disease appearance
- Provincial variety guides with disease resistance ratings


